Having owned a number of generators — both portable and whole house — the question of “What is an inverter generator?” has come up a number of times. Here are some facts that will help you better understand how generators work and which is the best for your home.
What Is An Inverter Generator?
This is the most common question about generators aside from “How much power do I need?” and it makes sense because the concepts are a bit confusing.
An inverter generator, as the name suggests, inverts electricity in order to make it safer for the product in your home. The generator converts AC current into DC and then inverts it to AC, which means cleaner, more consistent power going into your home. This process happens at a lower RPM level than a normal generator, which means quieter operation and less engine maintenance.
Normal generators, which use an engine to convert gasoline to AC power using a process that is loud and that produces a lot of fumes and carbon monoxide. This power is acceptable for powering a home, but if you were to plug a sensitive device, like a computer, directly into the generator the spiky power output could cause problems and disruptions.
Even you don’t need “clean” power output inverter generators are still attractive to buyers and they have many positive qualities.
Why Buy An Inverter Generator?
When people ask “What is an inverter generator?” what they usually mean to ask is, “Why should I buy (or not buy) and inverter generator”?
These generators are, generally speaking, smaller, quieter, and more efficient than traditional engine generators. Inverter models are usually more expensive, but not by a huge margin, so they are still an option that many people consider.
Inverter generators are more expensive to buy, and the upfront costs do deter people, but they are cheaper to operate over the long run thanks to better fuel efficiency and less engine maintenance.
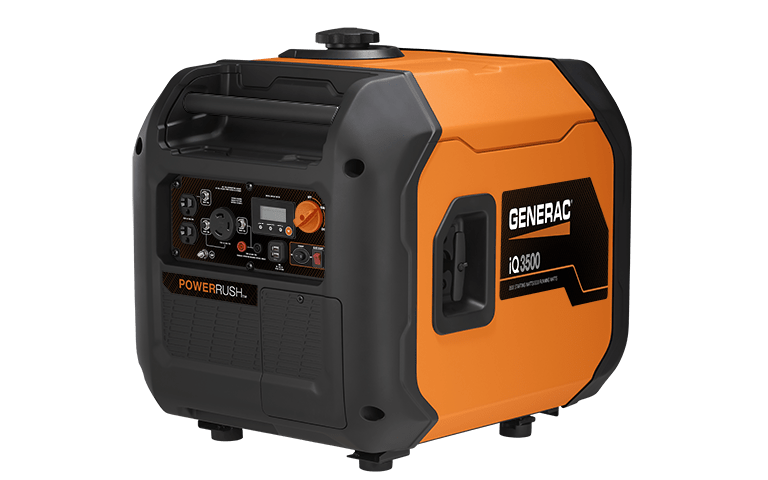
One popular inverter generator is the Generac IQ3500. It has the following specs:
- Running output of 3000W
- Maximum output of 3500W,
- Retail price of $1300
- Total harmonic distortion (THD) of 3%
- Total weight is 109 pounds
- Run time at 50% load is 8.9 hours using 2.6 gallons of fuel which means 5135 Wh/gallon
And now let’s look at the larger conventional model, the Generac GP3300 49 ST. This is a good comparison because the output power is the same.
- Running output of 3300W
- Maximum output of 3750W
- Retails price of $440
- Total harmonic distortion is not listed, but said to be under 25%
- Total weight is 101 pounds
- Run time at 50% load is 10.5 hours using 3.35 gallons which means 4682 Wh/gallon
But the real efficiency gains aren’t a result of an inverter running at the same 50% level as a traditional generator, but rather that the inverter can run at variable loads better than a normal generator. Inverters can adjust their engine RPM level (their speed) where a traditional generator only has one speed. So if you need less power the inverter will run slower, not push itself as hard, produce less current, and save gasoline.
Another advantage of inverter generators is that they can easily be run in parallel. To do this you need two inverter generators, which can be connected for twice the power output. This is usefully since small generators are so much easier to move and more affordable than larger ones.
Downsides of Inverters
We already known inverters are more expense upfront than a traditional engine generator and that you are paying more for each watt of output you are getting. There are some other downsides as well.
One big one is that inverters don’t really get that big. A larger portable generator, like the Generac GP15000E, might produce 15,000W watts when running. That’s a lot of power! The biggest inverter generator for homes sold these days is the Honda Ultra Quiet EU7000, a 7000W inverter generator. And this $4500 beast isn’t common, most inverter generators max out around the 3000W mark.
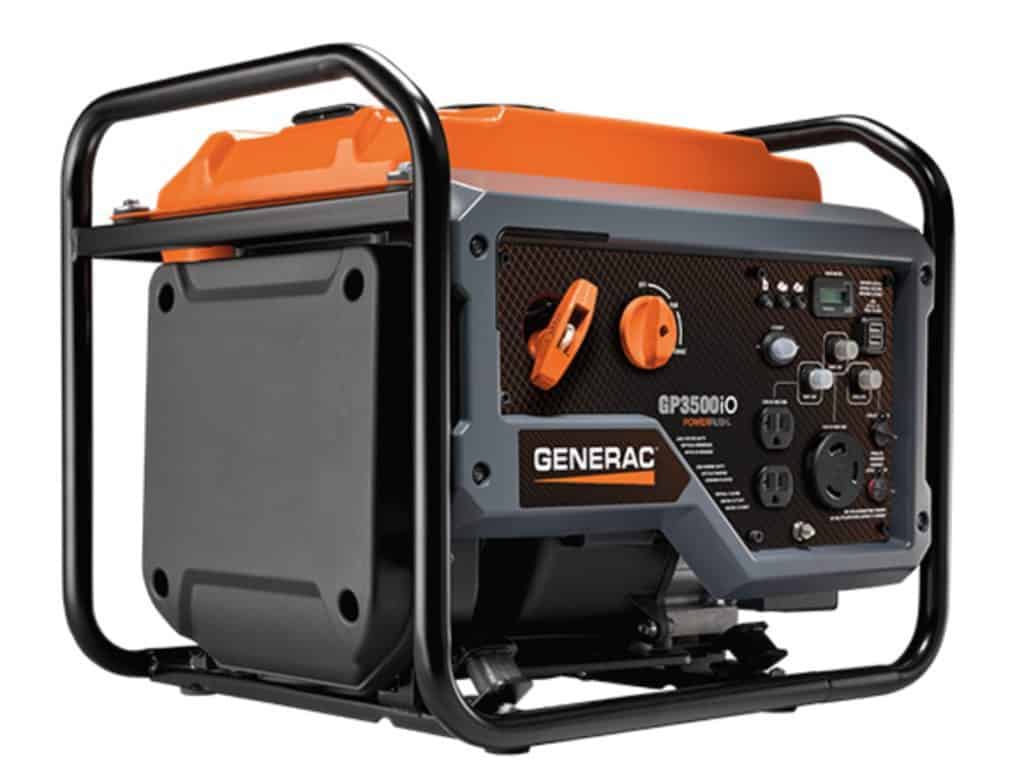

Why Do Inverters Look Different?
More inverter generators look like modern appliances — rounded and sort of plastic-y. This is strange when compared to a typical portable generator, which (after 3000W or so) looked like an engine that is surrounded by some metal tubing.
This metal tube design is known as an “open frame” generator and some inverter generators actually do use it, like the Generac GP3500iO. The open frame design is used when it no longer makes sense to put a surrounding over the entire generator, usually because it’s too large to easily support such a housing.
Most inverter generators are relatively small and light, since they are efficient and most are under 3000W. This means it makes sense to make them easy to carry and friendly to put in your car trunk, surrounded by your stuff. This would not work with an open frame generator, which collects grime easily, is hard to clean, and has an exposed muffler.
Also, keep in mind that most inverter generators lack wheels and are designed to be carried place to place. Open frame, conventional generators over 3000W usually have wheels and are rolled from place to place.
FAQs
Can inverter generators run indoors?
No. Inverter generators are cleaner, smaller, and quieter than conventional engine generators, but they are still engines that run on gasoline and emit fumes and carbon monoxide. For this reason they must only be run outdoors and sufficiently far from bedrooms and other living spaces.